Migration has always been a significant factor in shaping the workforce of any country. According to the ILO Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers, there were 169 million international migrant workers in 2019, accounting for 4.7% of the global labor force.
Also the Pew Research Center projects that the U.S. labor force will grow by up to 183.2 million till 2035, but only if immigration levels remain steady. Yet without immigration, the labor force would potentially shrink, as the baby boomer generation retires in hordes.
Key Takeaways
- Migration shapes the global workforce, with 169 million international migrant workers in 2019, constituting 4.7% of the global labor force, playing a pivotal role in economic growth and diversity.
- Immigrants in the US contributed $2 trillion to the U.S. GDP in 2016 and added $458.7 billion in taxes in 2018, playing key roles in service, construction, and high-skill occupations while significantly impacting entrepreneurship.
- Immigration affects labor market tightness. Recent data shows a strong rebound in immigration, helping to address labor shortages and loosening labor markets.
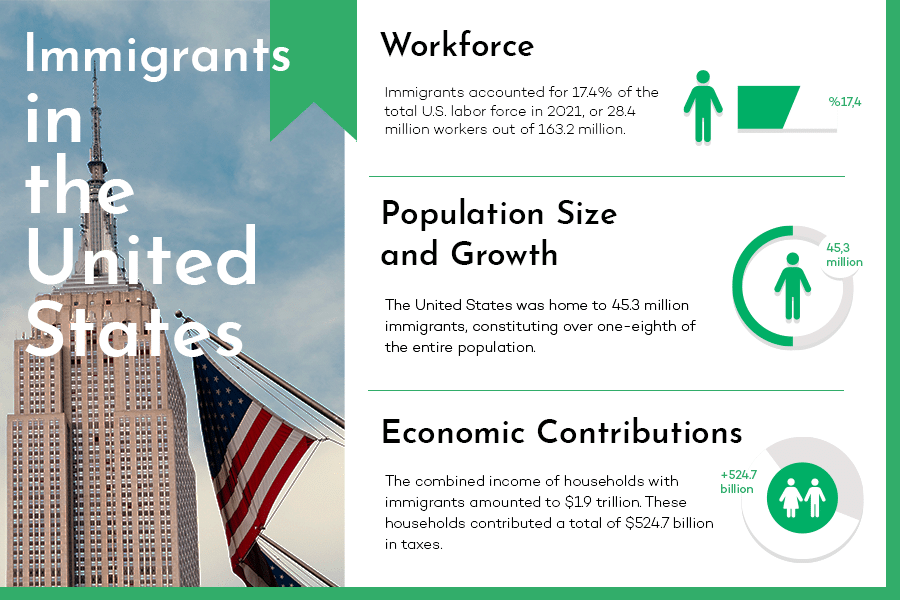
- The immigrant workforce constitutes 18.1% of the U.S. civilian labor force in 2022, projected to help fill 4.7 million jobs amid a labor shortage.
- Business owners should consider hiring immigrants for their diverse skills, ability to fill labor gaps, economic contribution, entrepreneurship, and strong work ethic.
The OECD reports that migration contributes to economic growth, innovation, and diversity in destination countries, as well as providing remittances and skills transfers to origin countries.
With such importance and impact, it is imperative to look deep down into the role of migration in the workforce, focusing on the latest data, and emphasizing how the immigrant workforce could be the solution for the labor force shortage in the US.
The Immigrant Workforce: A Complementary Role
Immigrants wield a fundamental influence in the U.S. economy. According to BLS, the foreign born accounted for 18.1 percent of the U.S. civilian labor force in 2022, up from 17.4 percent in 2021.
Between 2022 and 2032, the U.S. economy is expected to witness an increase of approximately 4.7 million jobs. In face of the labor shortage, it is immigrant workers who can help fill these jobs, which otherwise would remain vacant.
How the Immigrant Workforce Contributes to the Labor Market
- In 2016, immigrants generated $2 trillion for the U.S. GDP, and their tax contributions to state, local, and federal coffers amounted to $458.7 billion in 2018.
- Immigrants are more likely to work in service industry jobs, natural resources, construction and maintenance jobs, than those born in the U.S.
They also held more jobs than their American counterparts in natural resource, construction and maintenance occupations (13.9% versus 7.9%) and production, transportation and material moving occupations (15.2% versus 12.1%). - Immigrants contributed to 17% of the United States’ economic output (GDP), surpassing their share in the population.
- The share of immigrants in high-skill, nonmechanical jobs has risen in recent decades; such as their increased share in high-analytical-skill jobs, from 19% to 24% over the period of 1995 to 2018, and from 26% to 30% in jobs involving social skills.
- In 2022, the labor force participation rate (LFPR) remained significantly higher for foreign-born men (immigrants) at 77.4 percent compared to their native-born counterparts at 66.0 percent. Conversely, foreign-born women had a participation rate of 55.0 percent, slightly lower than the 57.2 percent rate for native-born women.
- Most Americans (about 77% of adults) believe that immigrants primarily take on jobs that U.S. citizens are generally not inclined to pursue (most often the low-skilled jobs).
These data points suggest that immigrants play a crucial role in the U.S. economy and are expected to become increasingly central to the U.S. economy given the current trends in occupation growth.

The Impact of Immigration on Labor Market Tightness
According to a report by the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, immigration flows into the United States slowed significantly following immigration policy changes from 2017 to 2020 and the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This migration slowdown tightened local labor markets, raising the ratio of job vacancies to unemployed workers (the V–U ratio) by 5.5 percentage points between 2017 and 2021.
The more recent data show that immigration has rebounded strongly, helping to close the shortfall in foreign-born labor and ease tight labor markets. Immigration contributes to labor force growth, and historically, it has tended to loosen labor markets by increasing the number of potential workers.
However, the impact of immigration on labor market tightness varies across states and industries, depending on the degree of exposure to foreign workers and the substitutability between native and foreign workers. States and industries with higher shares of foreign workers tend to have lower vacancy rates and vice versa.

Immigrants: The Solution to Labor Shortage in the US
Immigration can play a significant role in addressing the labor shortage in the United States. According to a report by the American Immigration Council, the U.S. is facing a labor crisis with job openings hitting an 11.5 million record high in March 2022.
The report suggests that immigrant workers can help meet labor demands and steer the U.S. economy back on track.
The data reveals that the most in-demand jobs are expected to continue to outpace the supply of available labor in the near term. In the year 2030, millions of extra workers (~2.9 million more) will be required to fill both newly created positions and those left vacant by retiring employees.
The widening disparity between the demand for labor and the decreasing pool of U.S.-born workers implies a necessity for an increased influx of foreign workers to bridge the resulting gap.
Moreover, occupations that grew the most between 2019 to 2021 were the ones with large shares of immigrants. U.S.-born workers are more likely than foreign-born workers to reach retirement age, and younger workers are more likely to be foreign-born.
Why Business Owners Should Consider Hiring Immigrants
Business owners in the US should consider hiring immigrant workers for several reasons:
Diverse Skills and Perspectives
Immigrants bring a wide range of skills, experiences, and perspectives that can foster innovation and creativity in the workplace.
Filling Labor Gaps
Immigrants can help meet the demand for workers in sectors that face labor shortages. Moreover, It is observed that immigrants are not as selective as US-born labor force to seek employment opportunities in rural areas or small cities within the United States.
Boosting the Economy
Immigrants contribute significantly to the economy. In 2021, immigrant households earned $1.9 trillion, paying $524.7 billion in taxes (with $346.3 billion federal and $178.4 billion state/local) and held $1.4 trillion in spending power.
Work Ethic and Motivation
Immigrants often display a strong work ethic and motivation, as they are willing to take on jobs that are in high demand but low supply.
By hiring immigrant workers, business owners can not only address immediate labor needs but also contribute to the long-term growth and competitiveness of their businesses.
Read more: The Declining Labor Force Participation in the Post-Pandemic US
Wrapping Up
To conclude, migration plays a vital role in shaping the workforce. Immigrants not only fill gaps in the labor market but also contribute to economic growth and development. The recent labor shortage in the U.S. has highlighted the importance of immigrants in the workforce.
As the data suggests, increasing immigration could be a viable solution to the current labor shortage in the U.S. Therefore, it is crucial to acknowledge and appreciate the role of immigrants in the workforce and businesses should consider their integration into the labor market.